How to troubleshoot
🚨 IMPORTANT 🚨
-
If you suspect a bug and haven't tested the
nightlybuild yet, install it to see if the issue persists. Instructions can be found here. -
If the logs aren't providing enough information, change the logging level from
INFOtoDEBUGin the config file. Learn how to edit theconfig.inihere. -
Review the CHANGELOG for any breaking changes and necessary configuration updates.
How the driver works
-
During installation (
execution of enable.sh) the enabling script creates a configuration file (/data/conf/serial-starter.d/dbus-serialbattery.conf) for theserial starter. This allows theserial starterto create services fordbus-serialbattery, if a new serial adapter is connected. Theserial starterservice (/service/serial-starter) then creates a service (/service/dbus-serialbattery.*) for each found serial port.Additionally during installation a service (
/service/dbus-blebattery.*) for each Bluetooth BMS and (/service/dbus-canbattery.*) for each CAN BMS is created. -
Each created service in
/service/dbus-serialbattery.*,/service/dbus-blebattery.*or/service/dbus-canbattery.*runs/data/apps/dbus-serialbattery/start-serialbattery.sh *.-
For
dbus-serialbatterythe*stands for the serial port, e.g. the service/service/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0runs/data/apps/dbus-serialbattery/start-serialbattery.sh ttyUSB0. -
For
dbus-blebatterythe*stands for an incremental number, e.g. the service/service/dbus-blebattery.0runs/data/apps/dbus-serialbattery/dbus-serialbattery.py Jkbms_Ble C8:47:8C:00:00:00, where the BMS typeJkbms_Bleand the BMS Bluetooth MAC addressC8:47:8C:00:00:00is fetched from the config file during installation. -
For
dbus-canbatterythe*stands for the can port, e.g. the service/service/dbus-canbattery.can0runs/data/apps/dbus-serialbattery/start-serialbattery.sh can0, where the CAN portcan0is fetched from the config file during installation.
-
Driver log files
Require root access
💡 If you are opening an issue or posting your logs somewhere please make sure you execute the complete commands to get the logs, including
tai64nlocal. Without readable timestamps we cannot help you.
Check the log files on your GX device/Raspberry Pi. Connect to your Venus OS device using a SSH client like Putty or bash.
The logfiles have a different location depending on the used connection:
Serial BMS connection
There are TWO log files that are relevant for the serial connection. Please check both.
/data/log/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB*/currentor/data/log/dbus-serialbattery.ttyAMA0/current/data/log/serial-starter/current(you need to check that only if the above log does not exist, is empty or outdated)
/data/log/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB*/current or /data/log/dbus-serialbattery.ttyAMA0/current
Where * is the number of your USB port (e.g. ttyUSB0, ttyUSB1, ttyUSB2, ...) or ttyAMA0, if you are using a Raspberry Pi hat.
Execute
💡 The tail command with the parameter -F does not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries.
You can exit by pressing CTRL + C.
tail -F -n 100 /data/log/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0/current | tai64nlocal
Output
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Starting dbus-serialbattery
INFO:SerialBattery:Venus OS v3.40
INFO:SerialBattery:dbus-serialbattery v1.3.0
INFO:SerialBattery:-- Testing BMS: 1 of 3 rounds
INFO:SerialBattery:Testing BMS_NAME
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Connection established to BMS_NAME
INFO:SerialBattery:Battery BMS_NAME connected to dbus from /dev/ttyUSB0
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Serial Number/Unique Identifier: UNIQUE_IDENTIFIER
...
✅ This indicates, that your driver started successfully and connected to your BMS. You can see now the BMS in the GUI.
❌ If you see an error like below, then your battery is most likely connected to a different ttyUSB port.
ERROR:SerialBattery:ERROR >>> No battery connection at /dev/ttyUSB0
/data/log/serial-starter/current
Serial starter will show, if the driver was started against a USB port.
Execute
💡 The tail command with the parameter -F does not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries.
You can exit by pressing CTRL + C.
tail -F -n 100 /data/log/serial-starter/current | grep dbus-serialbattery | tai64nlocal
Output
...
INFO: Create daemontools service dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0
INFO: Start service dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0 once
...
✅ This indicates, that the driver was successfully started against the USB0 port.
❌ If there is no dbus-serialbattery.tty* entry check with lsusb, if your USB to serial converter is recognized from Venus OS.
Here are some partial lsusb outputs which show a few different adapters. If you have attached only one adapter you will see only one similar entry as below:
Bus 001 Device 002: ID 0403:6015 Future Technology Devices International, Ltd Bridge(I2C/SPI/UART/FIFO)
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 0403:6001 Future Technology Devices International, Ltd FT232 Serial (UART) IC
Bus 001 Device 004: ID 0403:6015 Future Technology Devices International, Ltd Bridge(I2C/SPI/UART/FIFO)
Bus 001 Device 005: ID 0403:6011 Future Technology Devices International, Ltd FT4232H Quad HS USB-UART/FIFO IC
Bus 002 Device 002: ID 1a86:7523 QinHeng Electronics HL-340 USB-Serial adapter
Bluetooth BMS connection
/data/log/dbus-blebattery.*/current
Where * is an incremental number.
Execute
💡 The tail command with the parameter -F does not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries.
You can exit by pressing CTRL + C.
tail -F -n 100 /data/log/dbus-blebattery.*/current | tai64nlocal
Output
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Starting dbus-serialbattery
INFO:SerialBattery:Venus OS v3.40
INFO:SerialBattery:dbus-serialbattery v1.3.0
INFO:SerialBattery:init of BMS_NAME at BMS_MAC_ADDRESS
INFO:SerialBattery:test of BMS_NAME at BMS_MAC_ADDRESS
INFO:SerialBattery:BMS_NAME found!
INFO:SerialBattery:Connection established to BMS_NAME
INFO:SerialBattery:Battery BMS_NAME connected to dbus from BMS_MAC_ADDRESS
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Serial Number/Unique Identifier: UNIQUE_IDENTIFIER
...
✅ This indicates, that your driver started successfully and connected to your BMS. You can see now the BMS in the GUI.
❌ If you see an error like below, then your battery is not found.
INFO:SerialBattery:Starting dbus-serialbattery
INFO:SerialBattery:dbus-serialbattery v1.0.0
INFO:SerialBattery:init of BMS_NAME at BMS_MAC_ADDRESS
INFO:SerialBattery:test of BMS_NAME at BMS_MAC_ADDRESS
ERROR:SerialBattery:no BMS found at BMS_MAC_ADDRESS
ERROR:SerialBattery:ERROR >>> No battery connection at BMS_NAME
CAN BMS connection
/data/log/dbus-canbattery.*/current
Where * is the number of your CAN port (e.g. can0, can5, can9, ...).
Execute
💡 The tail command with the parameter -F does not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries.
You can exit by pressing CTRL + C.
tail -F -n 100 /data/log/dbus-canbattery.*/current | tai64nlocal
Output
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Starting dbus-serialbattery
INFO:SerialBattery:Venus OS v3.40
INFO:SerialBattery:dbus-serialbattery v1.3.0
INFO:SerialBattery:-- Testing BMS: 1 of 3 rounds
INFO:SerialBattery:Testing BMS_NAME
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Connection established to BMS_NAME
INFO:SerialBattery:Battery BMS_NAME connected to dbus from can0
...
INFO:SerialBattery:Serial Number/Unique Identifier: UNIQUE_IDENTIFIER
...
✅ This indicates, that your driver started successfully and connected to your BMS. You can see now the BMS in the GUI.
❌ If you see an error like below, then your battery is most likely connected to a different can port.
ERROR:SerialBattery:ERROR >>> No battery connection at can0
What to check, if it doesn't work
The log file will tell you what the driver did and where it failed.
No log file
If there is no log folder under /data/log/dbus-serialbattery.* then check:
-
Did the install have any error? Reinstall the driver, also trying an alternative method and version.
-
Is the connection picked up by serial-starter?
💡 The
tailcommand with the parameter-Fdoes not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries. You can exit by pressingCTRL + C.Use the command
tail -F /data/log/serial-starter/current | tai64nlocalto show the last part of the log file as it updates. Plug your USB device in and out to see, if it's picked up and what
ttyUSBport it uses.You can also check, which USB port it used by plugging out your USB device, wait some seconds, execute the command below, plug in your USB device, execute the command below again and compare which
ttyUSBdevice appeared now.Execute
ls -l /dev/ttyUSB*Example output (USB device unplugged)
crw-rw---- 1 root dialout 188, 0 Jun 11 17:08 /dev/ttyUSB0Example output (USB device plugged)
crw-rw---- 1 root dialout 188, 0 Jun 11 17:08 /dev/ttyUSB0
crw-rw---- 1 root dialout 188, 1 Jun 11 17:08 /dev/ttyUSB1 -
Did the serial starter correctly assign the USB port to the correct service?
If the content under
==> /data/var/lib/serial-starter/* <==showssbatterythen this USB port is assigned to thedbus-serialbatterydriver.Execute
head /data/var/lib/serial-starter/*Output
==> /data/var/lib/serial-starter/ttyACM0 <==
gps
==> /data/var/lib/serial-starter/ttyUSB0 <==
vedirect
==> /data/var/lib/serial-starter/ttyUSB1 <==
sbattery
==> /data/var/lib/serial-starter/ttyUSB2 <==
vedirectIf the assignment is wrong you can reset all executing this command
rm /data/var/lib/serial-starter/*and then reboot. You can also overwrite an assignment by executing the command below. Change the
#with the number of your USB port before executing the command. Reboot after the change.echo "sbattery" > /data/var/lib/serial-starter/ttyUSB# -
Check, if your BMS type is found (change to the
ttyUSB*your device use)-
For serial connected BMS
💡 The
tailcommand with the parameter-Fdoes not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries. You can exit by pressingCTRL + C.tail -F /data/log/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0/current | tai64nlocalor
tail -F /data/log/dbus-serialbattery.*/current | tai64nlocalto check all devices the serialstarter started.
-
For Bluetooth connected BMS
💡 The
tailcommand with the parameter-Fdoes not quit automatically, since it waits for new log entries. You can exit by pressingCTRL + C.tail -F /data/log/dbus-blebattery.0/current | tai64nlocalor
tail -F /data/log/dbus-blebattery.*/current | tai64nlocalto check all Bluetooth devices.
-
No reply in log file
Check your cable connections, if the log file shows ERROR: No reply - returning from the battery.
The RX/TX lights should both flash as data is transfered. If only one flashes then your RX/TX might be swapped.
Driver runtime (stability check)
Check for how long the driver is running without restart.
Execute
For serial connected BMS
svstat /service/dbus-serialbattery.tty*
For Bluetooth connected BMS
svstat /service/dbus-blebattery.*
Output
root@raspberrypi2:~# svstat /service/dbus-serialbattery.*
/service/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0: up (pid 8136) 1128725 seconds
✅ If the seconds (runtime) have a high number (e.g. several days; 86400 seconds = 1 day) then this indicates, that your driver is stable.
❌ If the seconds (runtime) are low (e.g. 300 seconds) then this means your driver has (re)started 300 seconds ago.
Check again in a few minutes, if the pid changed and if the runtime increased or reset.
If that is the case, your driver is not stable and has a problem.
root@raspberrypi2:~# svstat /service/dbus-serialbattery.*
/service/dbus-serialbattery.ttyUSB0: up (pid 8136) 300 seconds
Additionally you can check the system uptime.
Execute
uptime
Output
10:08:14 up 8 days, 3:24, load average: 1.52, 0.87, 0.79
Error codes
#8 Internal calculation error
Some calculation errors occured in the driver. Check the driver logs for more details.
#119 Settings invalid
Some settings in your config.ini are invalid. Check the driver logs for more details.
Driver behavior problems
Battery charging/discharging problems
Open the remote console/GUIv2 and check the dbus-serialbattery - General page under the battery device.
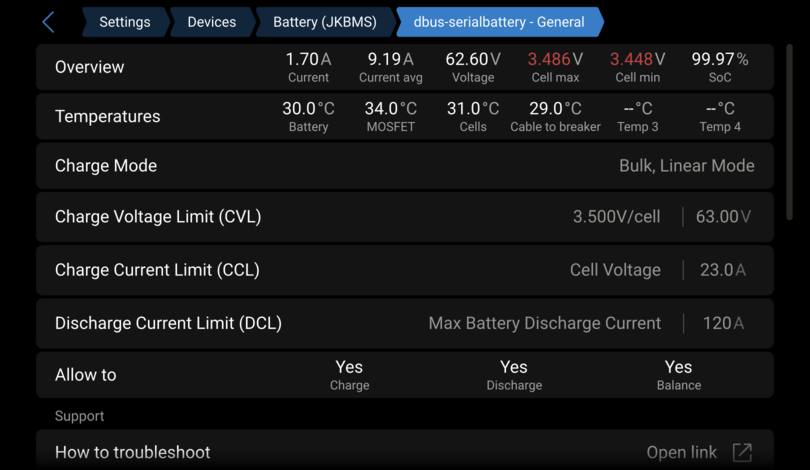
Here you see all relevant data of the driver.
-
Overview: Red values mean that they are limitingCVL,CCLorDCL. -
Temperatures: Red values mean that they are limitingCVL,CCLorDCL. -
Charge Mode: Here you see the active charge mode.Bulk,Absorption,Float Transition,FloatorKeep always max voltageis related to theCharge Voltage Limitation (affecting CVL)section in the config file.Cell OVP(Over Voltage Protection) is related to theCell Voltage Limitation (affecting CVL)section in the config file.SoC Resetis related to theSoC Reset Voltage (must match BMS settings)section in the config file.BalancingStep ModeorLinear Modeis related to theCharge Modesection in the config file.
-
Charge Voltage Limit (CVL): Here you see the maximum voltage per cell and for the whole battery. -
Charge Current Limit (CCL/DCL)andDischarge Current Limit: Here you see the parameter that most limits the current.Cell Voltageis related to theCell Voltage Current Limitation (affecting CCL/DCL)section in the config file.Temperatureis related to theTemperature Current Limitation (affecting CCL/DCL)section in the config file.SoCis related to theSoC Current Limitation (affecting CCL/DCL)section in the config file.BMSindicates if the current set in the BMS app is lower than the current set in the config file.
-
Allow to Charge/Discharge/Balance: If charging or discharging isNo, thenCCLorDCLis0. If that is not the case an alarm should be active and displayed in the field below. -
Alarms: This row only appears if there are active alarms. If multiple alarms are active, all of them will be shown here.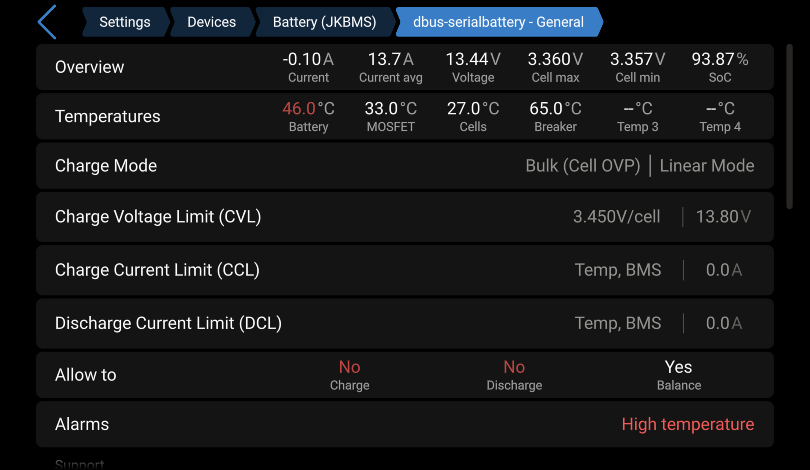
Charge mode problems
To better troubleshoot this make sure you have set this options in the config.ini. See How to edit the config.ini:
GUI_PARAMETERS_SHOW_ADDITIONAL_INFO = True
Now you see in the remote console/GUIv2 the driver internal values under the battery dbus-serialbattery - General page and you can check, why it's not working like it should.
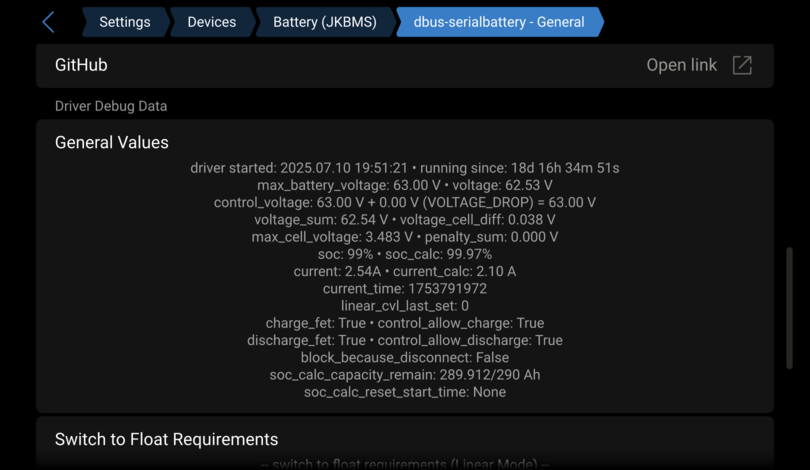
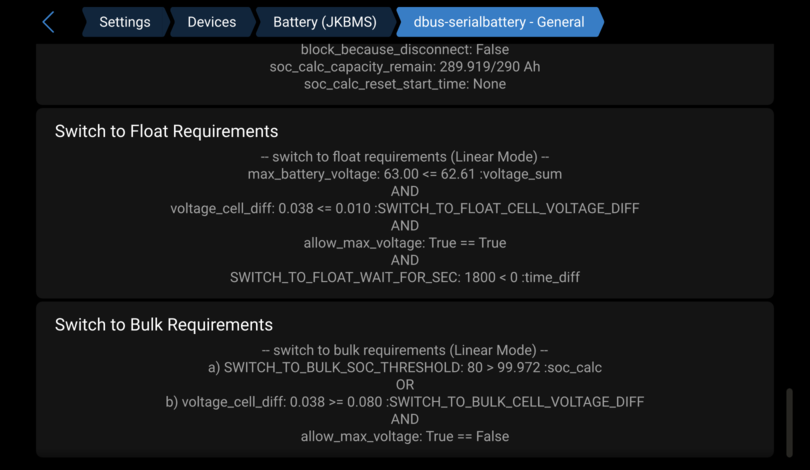
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Check the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) for answers
Alarm logs (VRM Portal)
Check your Alarm Logs in your VRM portal after selecting your device.
Advanced section (VRM Portal)
Check your graphs in Advanced section in your VRM Portal after selectiong your device.
You can use the graphs to look at your values over time. This makes finding values that change much easier.
- Battery SOC (State Of Charge)
- Battery Summary
- Battery Temperature Sensor
- Battery Voltage and Current
- BMS Charge and Discharge Limits
- BMS Min/Max Cell Voltage
Forum and community help
Forum thead discussions for this driver can be found at: