How to connect and prepare the battery/BMS
Make sure the data connection from the GX device to the BMS is isolated, see also galvanic isolation. Otherwise you can damage your GX device and BMS, since the negative current will flow through the data cable, if the BMS disconnects the negative pole.
Since for some BMS the port labeling is a mess and not reflecting the real situation here are some useful instructions and links.
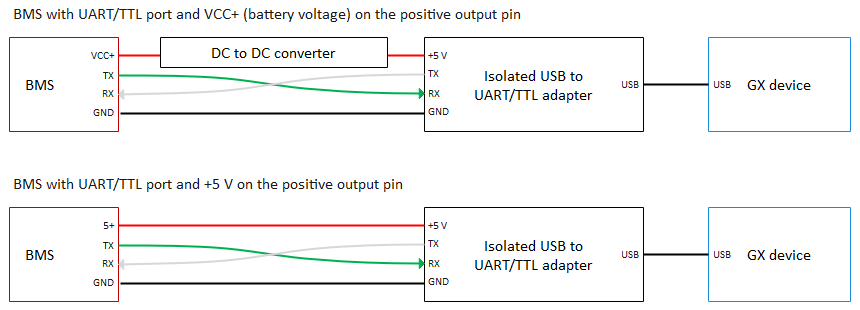
UART/TTL (no daisy chain possible)
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) is a serial communication protocol used for communication between devices. TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) refers to the voltage levels used in UART communication.
Ensure the voltage levels (5 V or 3.3 V) of your BMS are supported by the USB to UART/TTL adapter. Use an isolated adapter and power it correctly. Most BMS provide battery power VCC+ on the + pole of the UART/TTL connector. Measure it before connecting. You may need a DC to DC converter to match the voltage your isolated adapter needs.
Connect the wires in a device-to-device configuration. The main cable runs from the master (USB to UART adapter) to the BMS and contains three wires:
- TX (Transmit)
- RX (Receive)
- GND (common) for proper reference
The main cable should be shielded to prevent interference. Ensure that the TX of the master is connected to the RX of the BMS and the RX of the master is connected to the TX of the BMS.
Recommended adapters that are high quality and have been tested over a long period:
- USB SinglePort VE.Direct (affiliate link)
- USB Quadport VE.Direct (affiliate link)
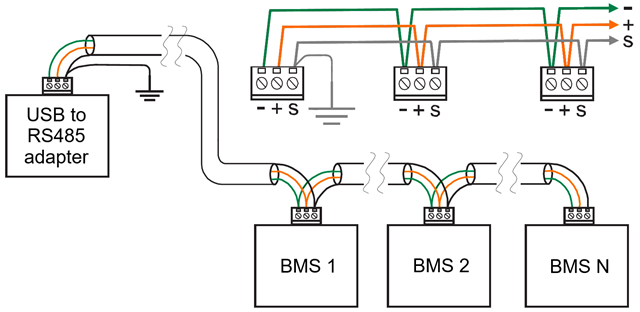
RS485/Modbus (daisy chain possible)
Refer to the feature comparison to see which BMS models support daisy chaining.
RS485 is a differential balanced line over twisted pair, capable of spanning up to a few hundred meters. Be aware of voltage drops due to cable resistance and sensor power consumption.
Connect the wires in a device-to-device (daisy chain) configuration:
- Avoid star or ring networks to prevent signal reflections.
- The main cable runs from the master (USB to RS485 adapter) to all BMS and contains three wires:
- A (DATA-)
- B (DATA+)
- GND (common) for proper reference
The main cable should be shielded. Ideally, the shield is separate from the 0 Volt line (GND), but they can be combined if the shield is free of voltage fluctuations.
Use a termination resistor (120-130 Ω) between A (DATA-) and B (DATA+) if the line is longer than 10 meters.
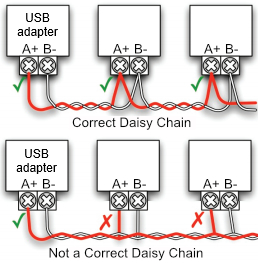
See also this page.
CAN (daisy chain possible)
Refer to the feature comparison to see which BMS models support daisy chaining.
Do not forget to set
CAN_PORTin theconfig.ini.
First, you need to create the correct cable.
Victron Side
Refer to the VE.Can to CAN-bus BMS cables manual for instructions.
⚠️ Remember to use a 120 Ω resistor between CAN-H and CAN-L, or use a VE.Can RJ45 Terminator to terminate the line. Otherwise, it won't work. In some cases, you may also need to terminate the other end of the line.
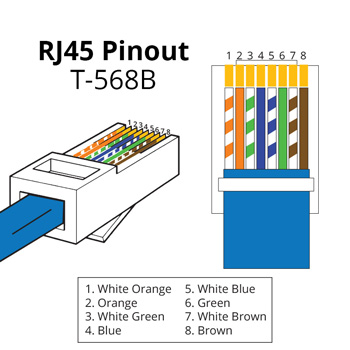
| Function | Victron VE.Can Side | RJ45 Pinout T-568A | RJ45 Pinout T-568B |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | Pin 3 | White/Orange | White/Green |
| CAN-H | Pin 7 | White/Brown | White/Brown |
| CAN-L | Pin 8 | Brown | Brown |
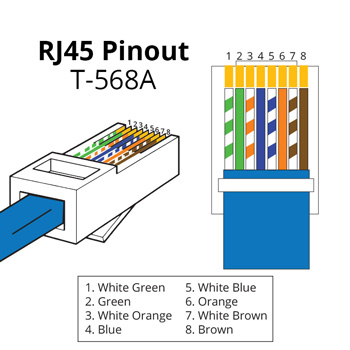
BMS Side
Check your BMS manual for the correct pinout. If you don't find any, you could try to measure the voltages.
| Function | Voltage to GND |
|---|---|
| GND | 0 V |
| CAN-H | +3 V |
| CAN-L | +2 V |
Daisy chain
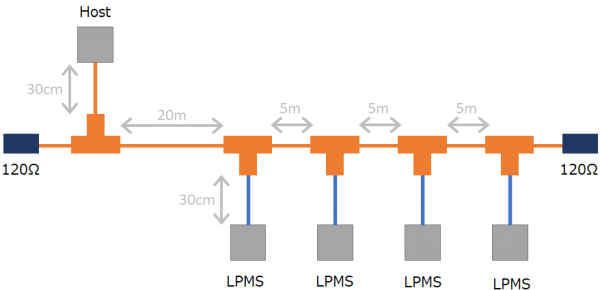
See also this page.
Bluetooth
No special preparation is required.
BMS configuration
Daly BMS
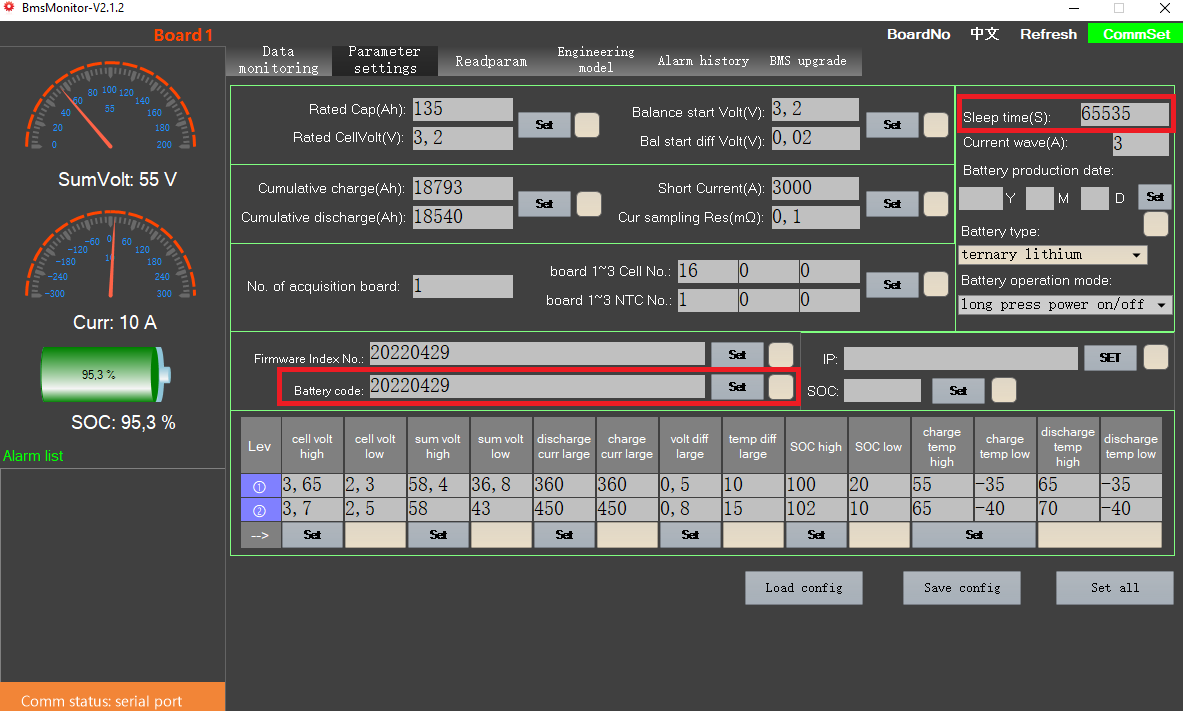
Connect your BMS via the PC software (BmsMonitor) and set the Sleep time(S) to 65535 to prevent the BMS from going to sleep.
If you are using multiple batteries you also have to make sure, that the Battery code is different on every battery.
RS485
🌼🔗 Only if you want to connect multiple Daly BMS to the same RS485 adapter 👇
-
Use Daly's BmsMonitor software (only for Windows) to set the board number. Using the mobile app
SMART BMSto set the board number will not correctly set it. -
Set a different board number for each BMS in the
BMS Toolssoftware -
Specify the MODBUS addresses in the
config.iniat theBATTERY_ADDRESSESparameter.For example, if you are using three batteries the parameter would be
BATTERY_ADDRESSES = 0x40, 0x41, 0x42.board number modbus address 10x4020x4130x4240x4350x4460x4570x4680x4790x48100x49110x4a120x4b130x4c140x4d150x4e160x4f
CAN
🌼🔗 Only if you want to connect multiple Daly BMS to the same CAN port 👇
- Download the Software
-
Visit this link and download the "PC Host Program for BMS."
-
Extract the downloaded file and run
JHB_serialport.exe.Note: Windows may block the program. If so, override the warning to proceed.
- Start the Software
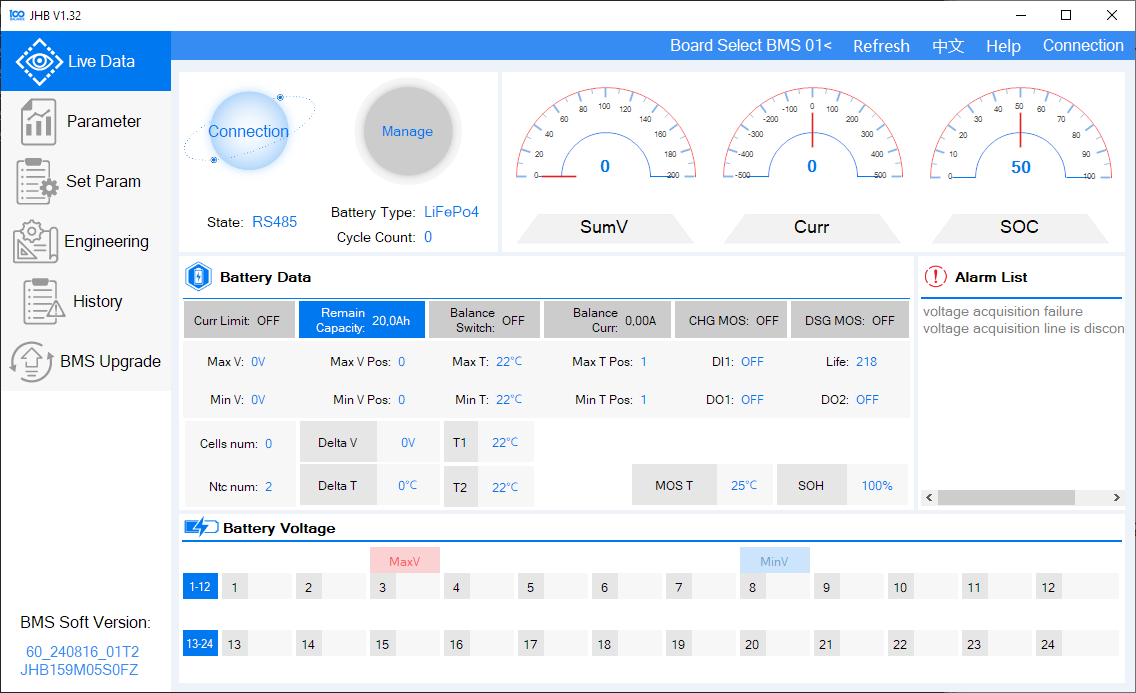
-
After launching the program, the main screen should look like this:
- Establish the Connection
-
Select the appropriate connection method:
-
If you don’t have a compatible CAN adapter for your PC, use an RS485 adapter instead.
-
Choose the RS485 adapter from the serial port selection and set the baud rate to
9600.Note: The Peak CAN USB dongle may not work with this version of the software. Alternatively, you can use the older "BMSTool-V1.14.23" software, which is more complex but compatible.
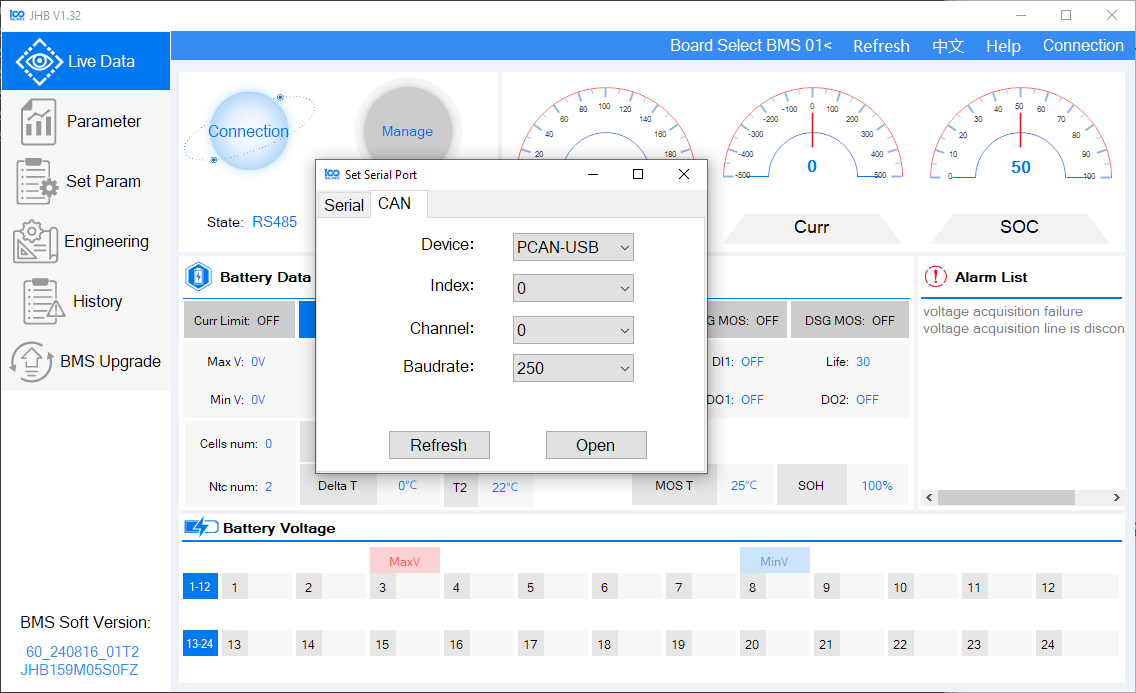
-
View Live Battery Data
- Once connected, you should see live values from your battery.
-
Set the Board Address
-
Navigate to the "Engineering" menu on the left.
-
Locate the Board Address Setting at the top-right corner of the screen.
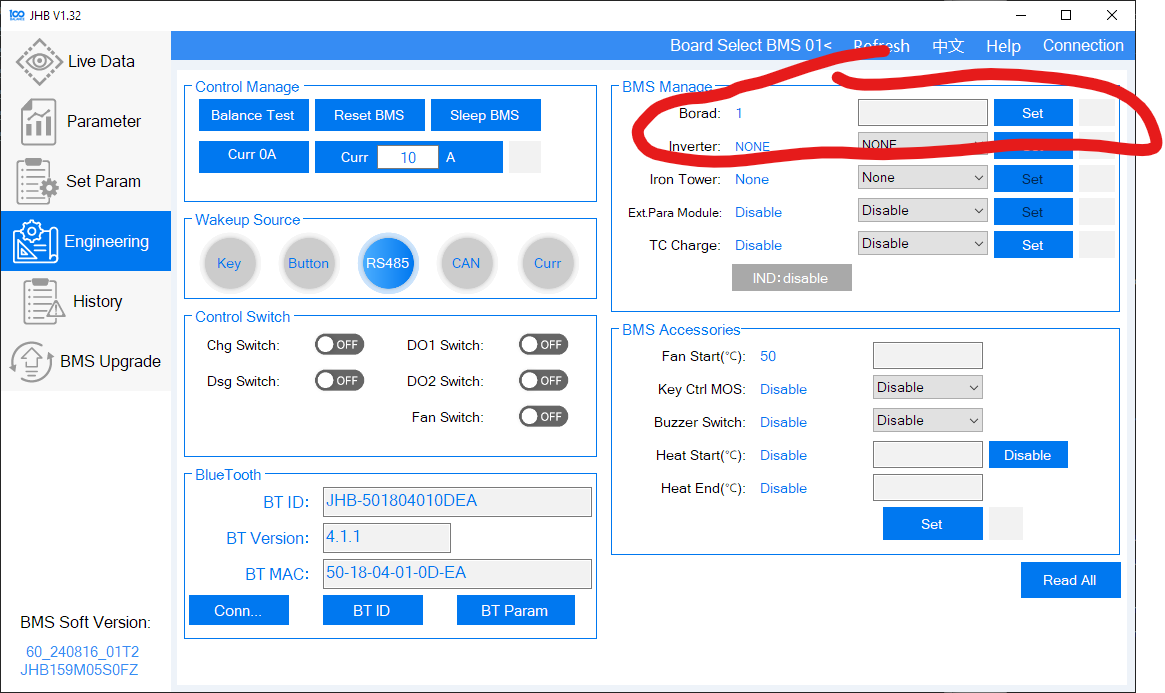
-
Enter your desired address and click "Set". A green checkmark will confirm the change.
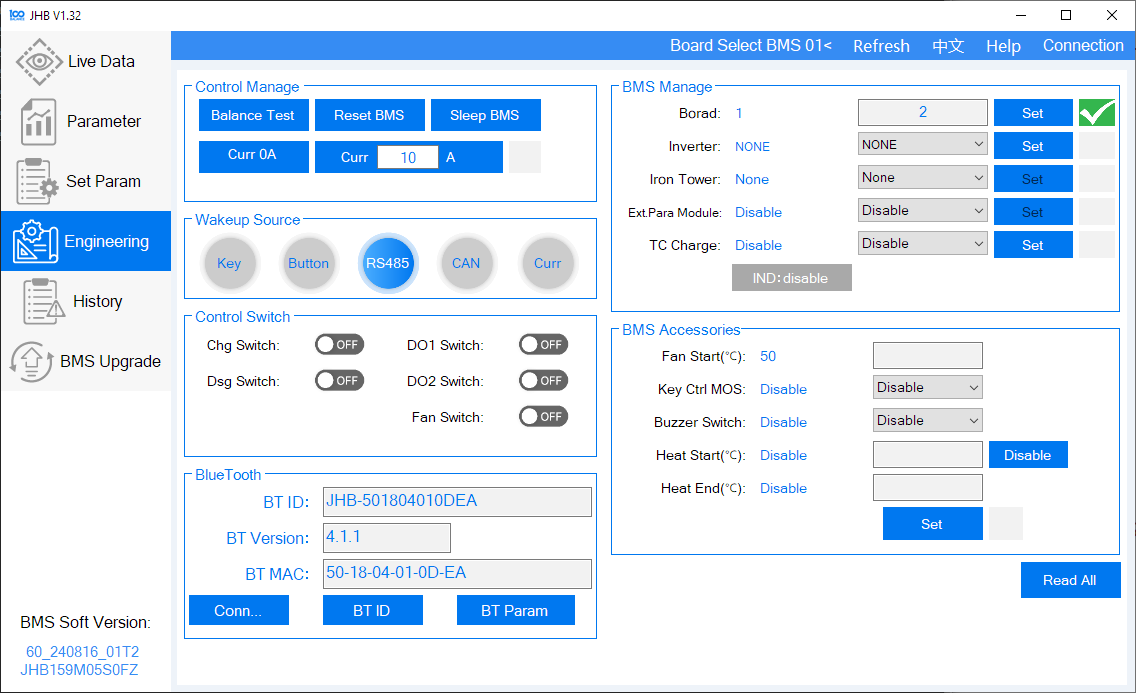
-
-
Verify the Address
-
Return to the Main Screen.
-
Select your board number from the address dropdown at the top. You should see live values again.
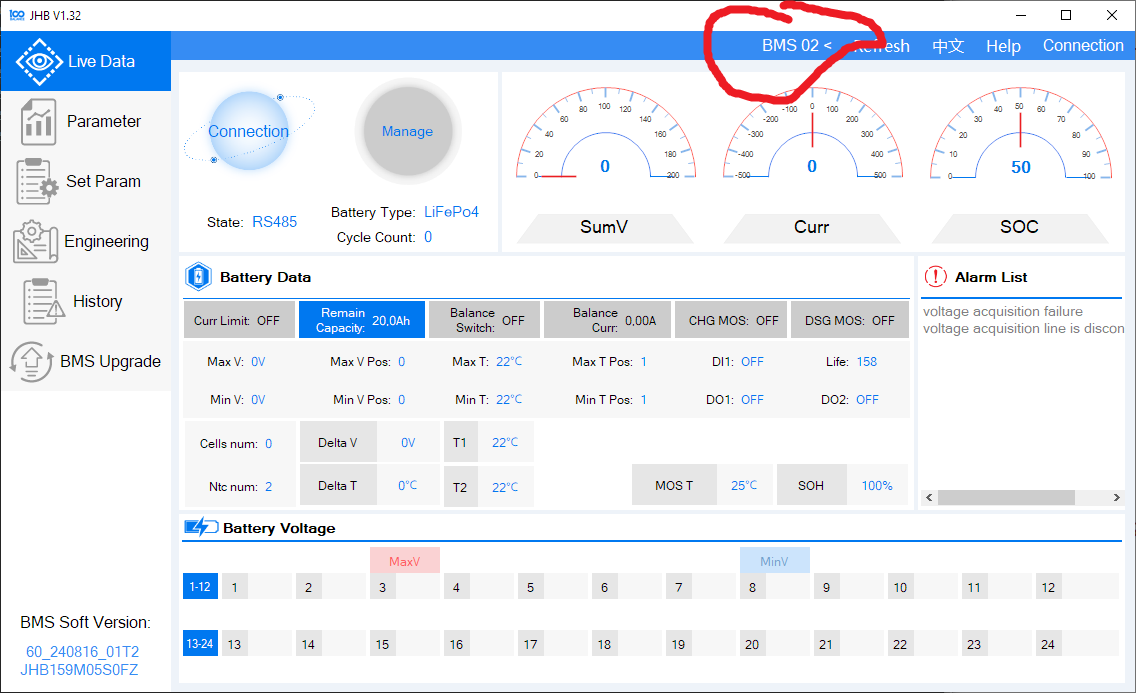
-
-
Specify the CAN addresses in the
config.iniat theBATTERY_ADDRESSESparameter.For example, if you are using three batteries the parameter would be
BATTERY_ADDRESSES = 0x40, 0x41, 0x42.Board number CAN address 10x0120x0230x0340x0450x0560x0670x0780x0890x09100x0a110x0b120x0c130x0d140x0e150x0f160x10
Daren 485
See daren-485 on GitHub.
EG4 LiFePower
Also valid for:
|- Revov
|- TianPower
Set your DIP switch pins to 1 for the battery connected to the Cerbo GX.
🌼🔗 Only if you want to connect multiple EG4 LiFePower to the same RS485 adapter 👇
Set different battery addresses for each battery using the dip switches and then specify the MODBUS addresses in the config.ini at the BATTERY_ADDRESSES parameter.
For example, if you are using three batteries (battery 1 dip switches: 1: ON, rest off, battery 2 dip switches: 1: OFF, 2: ON, rest off, battery 3 dip switches: 1: ON, 2: ON, rest off) the parameter would be BATTERY_ADDRESSES = 0x01, 0x02, 0x03.
| Dip switch position | MODBUS address |
|---|---|
1 2 3 4 | |
_ _ _ _ | 0x00 |
‾ _ _ _ | 0x01 |
_ ‾ _ _ | 0x02 |
‾ ‾ _ _ | 0x03 |
_ _ ‾ _ | 0x04 |
‾ _ ‾ _ | 0x05 |
_ ‾ ‾ _ | 0x06 |
‾ ‾ ‾ _ | 0x07 |
_ _ _ ‾ | 0x08 |
‾ _ _ ‾ | 0x09 |
_ ‾ _ ‾ | 0x0a |
‾ ‾ _ ‾ | 0x0b |
_ _ ‾ ‾ | 0x0c |
‾ _ ‾ ‾ | 0x0d |
_ ‾ ‾ ‾ | 0x0e |
‾ ‾ ‾ ‾ | 0x0f |
See also EG Lifepower (Narada battery that uses Tianpower BMS) - Multi battery setup problems.
JBD BMS
RS-485 connection is recommended because it provides more detailed information than what's available over CAN, such as individual cell voltages. One benefit of using CAN is that it requires only cables, not additional adapter hardware.
For UP series, this guide has detailed information on how to daisy-chain the batteries.
RS-485
With RS-485, your BMS_TYPE will most likely be autodetected as LltJbd, which is the default option that does not support daisy-chaining.
Information specific to UP series
If your JBD BMS is from UP16S series, you can manually set BMS_TYPE = LltJbd_Up16s in config.ini to enable support for daisy-chaining, CCL/DCL from the BMS and, depending on your setup, possibly cell balancing status and high-resolution SOC (0.01%). However, compared to LltJbd some BMS manipulation features will not be supported, see feature comparison to decide which option you prefer. The information below is for LltJbd_Up16s.
Battery addresses start from 1 (1 is the master) and you need to specify them in the config, e.g. BATTERY_ADDRESSES = 0x01, 0x02, 0x03.
Below are the possible cabling configurations in the descending order of how much information can be read from the BMSes. All of these configurations are supported, the differences are fairly minor and are described in the table. If unique BMS serial number cannot be read and a combination of "Pack SN Code" and rated battery capacity happens to be not unique among your batteries, dbus-serialbattery will refuse to work with those batteries. To workaround that, in the Config tab in JBD-ES-UP you can set Pack SN Code (sometimes labeled just "SN Code") to any unique text, or, as a secondary option, slightly change the Rated Capacity to make it unique.
| Configuration | Refresh interval, seconds | Read cell balancing status (2) | Read high-resolution SOC, cumulative Ah drawn, unique BMS serial number, full model, firmware version and production dates (3) | AUTO_RESET_SOC config.ini setting support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GX device connected with separate adapters directly to each BMS on RS485-1, RS232, or Bluetooth/Wifi UART port. In this (and only this) scenario set UP16S_REQUIRE_DIRECT_CONNECTION in config.ini to True, otherwise if your batteries are also connected through their ADD_IN/ADD_OUT ports you will either get duplicate batteries displayed, or not all the available data will be read. | ~1s | For all batteries | For all batteries | For all batteries |
| GX device connected only to the master through the Bluetooth/Wifi UART port on the BMS PCB, e.g. using the JBD UART Communication Module. Batteries are daisy-chained through their ADD_IN/ADD_OUT ports. | ~50s (1) | For master only | For all batteries | For all batteries |
| GX device connected only to the master through RS485-1 or RS232 (RS232 is untested), batteries are daisy-chained through their ADD_IN/ADD_OUT ports. | ~50s (1) | For master only | For master only | For master only |
(1) The refresh interval with daisy-chained batteries is limited by the master BMS. Master information still gets updated every ~1s.
(2) Cell balancing status for all daisy-chained batteries might be available on up-to-date firmware, but this hasn't been verified.
(3) High-resolution SOC and cumulative Ah drawn require firmware around v12 or later. For the full model, firmware version and production dates, you can verify these values are read successfully by checking whether BMS and Pack dates are shown for each of your batteries in Cerbo Settings -> Devices -> your battery -> Device -> Hardware Version.
CAN
With JBD, dbus-serialbattery currently supports only the Victron dialect of CAN protocol, so you'll need to change the CAN protocol in the BMS settings to "Victron". It's not clear whether any other JBD BMS than the UPxx series has this setting. If your BMS has a screen, the easiest way to do so might be on the screen, on the UP series go to PaskSet -> CANBus -> choose Can-Victron. Otherwise, JBD-ES-UP software for UP series has protocol dropdowns on the main screen. If "Set" buttons are inactive, click Account -> User Login in the menu and enter the password from the link. Some Bluetooth apps might also allow to set CAN protocol, but the PC software appears to be more well-maintained.
Note that JBD BMS over CAN is supported by Victron natively, so you don't need dbus-serialbattery if you just want communication with the BMS. However, dbus-serialbattery allows you to fine-tune the current and voltage parameters in such a way that BMS protection never has to be triggered, providing an additional layer of safety. Also, if your batteries are ever exposed to below room temperatures, you can set the charge current control based on temperature (CCCM_T_ENABLE) to more healthy values based on the datasheet for your cells, compared to the simple binary undertemperature cutoff that JBD BMS has.
JBD BMS CAN protocol support has been verified to work with UP16S015 through Type A cable connected to CAN1 port on the BMS.
JKBMS
The JKBMS unfortunately has a wrong labeling. Here the correct pinout.
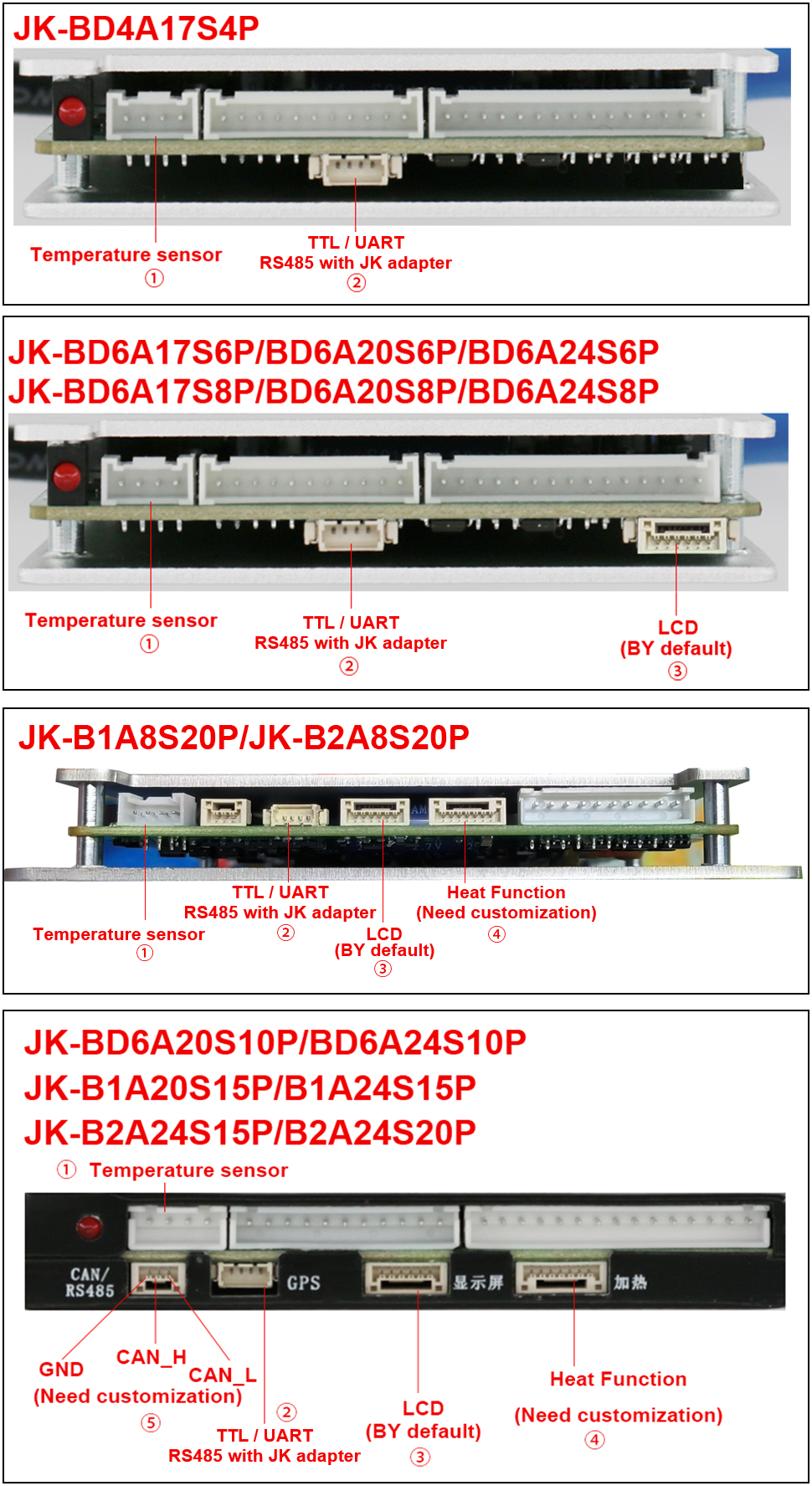
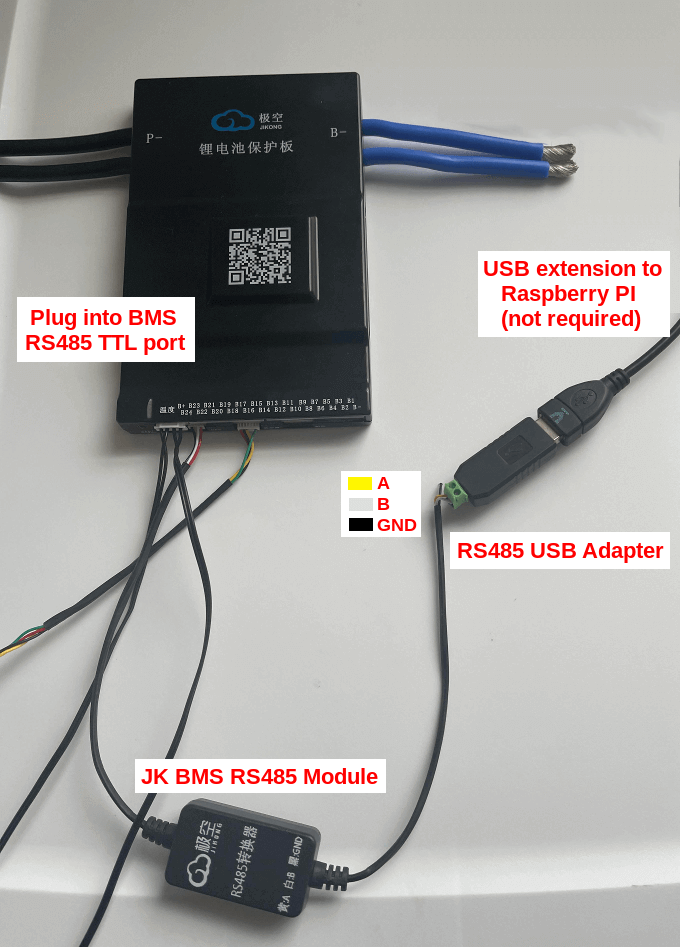
See also JK BMS JK-B2A8S20P RS-485 port / connector and New JKBMS "JK_DZ11B1A24S" (balancer only).
JKBMS PB Model (also know as JK Inverter BMS)
🌼🔗 Only if you want to connect multiple JKBMS PB BMS to the same RS485 adapter 👇
-
Give each battery a unique address using the jumper on the front. Do not use
_ _ _ _, which corresponds to address0x00, as it sets the BMS into master mode, disabling RS485 communication. Then specify the MODBUS addresses in theconfig.iniat theBATTERY_ADDRESSESparameter.For example, if you are using three batteries (battery 1 dip switches:
1: ON, rest off, battery 2 dip switches:1: OFF, 2: ON, rest off, battery 3 dip switches:1: ON, 2: ON, rest off) the parameter would beBATTERY_ADDRESSES = 0x01, 0x02, 0x03.dip switch position modbus address 1 2 3 4_ _ _ _0x00‾ _ _ _0x01_ ‾ _ _0x02‾ ‾ _ _0x03_ _ ‾ _0x04‾ _ ‾ _0x05_ ‾ ‾ _0x06‾ ‾ ‾ _0x07_ _ _ ‾0x08‾ _ _ ‾0x09_ ‾ _ ‾0x0a‾ ‾ _ ‾0x0b_ _ ‾ ‾0x0c‾ _ ‾ ‾0x0d_ ‾ ‾ ‾0x0e‾ ‾ ‾ ‾0x0f -
Use a ethernet/CAT cable to connect all batteries via the RS485-2 ports. Both RS485-2 ports can be used.
-
Connect the first battery to your Cerbo/Raspberry using the RS485 to USB cable that came with the BMS.
-
In the JKBMS App ensure that the UART Protocol is set to the default
0/1. -
Reboot the system to apply the changes.
See also Is anyone using the new style JK inverter BMS with dbus-serialbattery driver?.
Renogy
🌼🔗 Only if you want to connect multiple Renogy BMS to the same RS485 adapter 👇
-
Connect all batteries to the RS485 battery monitor or the BT2 to give the batteries individual addresses.
-
Disconnect the batteries from the RS485 battery monitor or the BT2 and connect them to the USB to RS485 adapter which is connected to the GX device.
-
Specify the MODBUS addresses in the
config.iniat theBATTERY_ADDRESSESparameter.For example, if you are using three batteries the parameter would be
BATTERY_ADDRESSES = 0x30, 0x31, 0x32.battery count MODBUS address 10x3020x3130x3240x3350x3460x3570x3680x3790x38100x39110x3a120x3b130x3c140x3d150x3e160x3f
See also Renogy - Multi battery setup documentation.
Generic MQTT battery data structure
This describes the JSON data structure needed for a generic MQTT driver. It covers all possible fields, their types, whether they are mandatory, and a short description for each.
Minimal example
{
"cell_count": 4,
"capacity": 100,
"serial_number": "SN12345678",
"voltage": 13.2,
"current": 5.2,
"soc": 45.87,
"temperature_1": 25.5,
"charge_fet": true,
"discharge_fet": true,
"cells": [
{ "voltage": 3.3 },
{ "voltage": 3.31 },
{ "voltage": 3.29 },
{ "voltage": 3.3 }
]
}
Full example
{
"balance_fet": true,
"capacity_remain": 80,
"capacity": 100,
"cell_count": 4,
"charge_fet": true,
"current": 5.2,
"custom_field": "Example custom value",
"discharge_fet": true,
"hardware_version": "v1.2",
"heater_fet": true,
"heating": false,
"heater_current": 2.05,
"heater_power": 27.06,
"heater_temperature_start": 2,
"heater_temperature_stop": 5,
"max_battery_charge_current": 50,
"max_battery_discharge_current": 60,
"max_battery_voltage_bms": 14.6,
"min_battery_voltage_bms": 10,
"production": "2025-12-25",
"serial_number": "SN12345678",
"soc": 45.87,
"soh": 98.5,
"temperature_1": 25.5,
"temperature_2": 25.6,
"temperature_3": 25.7,
"temperature_4": 25.8,
"temperature_mos": 30,
"voltage": 13.2,
"cells": [
{ "voltage": 3.3, "balance": false },
{ "voltage": 3.31, "balance": true },
{ "voltage": 3.29, "balance": false },
{ "voltage": 3.3, "balance": false }
],
"history": {
"deepest_discharge": -80.0,
"last_discharge": -40.0,
"average_discharge": -50.0,
"total_ah_drawn": -1200.0,
"charge_cycles": 120,
"timestamp_last_full_charge": 1766774400,
"full_discharges": 5,
"minimum_voltage": 10.5,
"maximum_voltage": 14.7,
"minimum_cell_voltage": 2.5,
"maximum_cell_voltage": 3.7,
"low_voltage_alarms": 2,
"high_voltage_alarms": 1,
"minimum_temperature": 15.0,
"maximum_temperature": 38.5,
"discharged_energy": 350,
"charged_energy": 360
},
"protection": {
"high_voltage": 0,
"high_cell_voltage": 0,
"low_voltage": 0,
"low_cell_voltage": 0,
"low_soc": 0,
"high_charge_current": 0,
"high_discharge_current": 0,
"cell_imbalance": 0,
"internal_failure": 0,
"high_charge_temperature": 0,
"low_charge_temperature": 0,
"high_temperature": 0,
"low_temperature": 0,
"high_internal_temperature": 0,
"fuse_blown": 0
}
}
Field Reference
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
cell_count | integer | Yes | Number of cells in the battery |
capacity | number (float/int) | Yes | Total battery capacity (usually in Ah) |
serial_number | string | Yes | Unique serial number of the battery |
voltage | number (float) | Yes | Total battery voltage (V) |
current | number (float) | Yes | Current flowing through the battery (A) |
soc | number (float) | Yes | State of charge in percent (0-100) |
temperature_1 | number (float) | Yes | Temperature from the first sensor (°C) |
charge_fet | boolean | Yes | Charging FET status (true=enabled, false=disabled) |
discharge_fet | boolean | Yes | Discharging FET status (true=enabled, false=disabled) |
cells | array of objects | Yes | List of cell objects (see below) |
balance_fet | boolean | No | Balancing FET status |
capacity_remain | number (float) | No | Remaining battery capacity (Ah) |
custom_field | string | No | Custom user-defined field |
hardware_version | string | No | Hardware version identifier |
heater_fet | boolean | No | Heater FET status |
heating | boolean | No | Heating status |
heater_current | number (float) | No | Current used by the heater (A) |
heater_power | number (float) | No | Power used by the heater (W) |
heater_temperature_start | number (float/int) | No | Heater start temperature (°C) |
heater_temperature_stop | number (float/int) | No | Heater stop temperature (°C) |
max_battery_charge_current | number (float) | No | Maximum allowed charge current (A) |
max_battery_discharge_current | number (float) | No | Maximum allowed discharge current (A) |
max_battery_voltage_bms | number (float) | No | Maximum battery voltage as reported by BMS (V) |
min_battery_voltage_bms | number (float) | No | Minimum battery voltage as reported by BMS (V) |
production | string (date) | No | Production date or code |
soh | number (float) | No | State of health in percent (0-100) |
temperature_2 | number (float) | No | Temperature from the second sensor (°C) |
temperature_3 | number (float) | No | Temperature from the third sensor (°C) |
temperature_4 | number (float) | No | Temperature from the fourth sensor (°C) |
temperature_mos | number (float) | No | MOSFET temperature (°C) |
history | object | No | Historical data (see below) |
protection | object | No | Protection/Alarm status (see below) |
cells Array
Each cell object contains:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
voltage | float | Yes | Voltage of the cell (V) |
balance | boolean | Yes | Whether the cell is being balanced |
history Object
Contains historical battery data:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
deepest_discharge | float | Deepest discharge recorded (Ah) |
last_discharge | float | Last discharge value (Ah) |
average_discharge | float | Average discharge value (Ah) |
total_ah_drawn | float | Total amp-hours drawn from battery (Ah) |
charge_cycles | int | Number of charge cycles |
timestamp_last_full_charge | int | Unix timestamp of last full charge |
full_discharges | int | Number of full discharges |
minimum_voltage | float | Minimum voltage recorded (V) |
maximum_voltage | float | Maximum voltage recorded (V) |
minimum_cell_voltage | float | Minimum cell voltage recorded (V) |
maximum_cell_voltage | float | Maximum cell voltage recorded (V) |
low_voltage_alarms | int | Number of low voltage alarms |
high_voltage_alarms | int | Number of high voltage alarms |
minimum_temperature | float | Minimum temperature recorded (°C) |
maximum_temperature | float | Maximum temperature recorded (°C) |
discharged_energy | float | Total discharged energy (Wh or kWh) |
charged_energy | float | Total charged energy (Wh or kWh) |
protection Object
Contains protection and alarm status flags. For all fields: 2 = Alarm, 1 = Warning, 0 = OK.
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
high_voltage | int | High voltage status |
high_cell_voltage | int | High cell voltage status |
low_voltage | int | Low voltage status |
low_cell_voltage | int | Low cell voltage status |
low_soc | int | Low state of charge status |
high_charge_current | int | High charge current status |
high_discharge_current | int | High discharge current status |
cell_imbalance | int | Cell imbalance status |
internal_failure | int | Internal failure status |
high_charge_temperature | int | High charge temperature status |
low_charge_temperature | int | Low charge temperature status |
high_temperature | int | High temperature status |
low_temperature | int | Low temperature status |
high_internal_temperature | int | High internal temperature status |
fuse_blown | int | Fuse blown status |
Notes
- All mandatory fields must be present for the data to be valid.
- Optional fields provide additional information if available.
- Types must match exactly (e.g., booleans for FETs, floats for voltages).
- The
cellsarray length must matchcell_count. - Timestamps are Unix epoch seconds.